The AI landscape is witnessing a transformative phase with the introduction of Starling-7B, a trailblazing large language model (LLM) developed by Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (RLAIF). This model is a significant stride in improving the performance of chatbots, harnessing the strengths of the GPT-4 labeled ranking dataset, Nectar, and innovative reward training and policy tuning techniques.
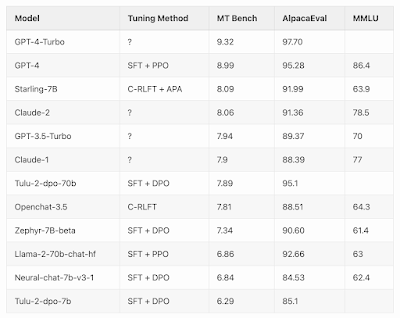
Starling-7B has achieved an impressive 8.09 score in MT Bench, outperforming most existing models, barring OpenAI’s GPT-4 and GPT-4 Turbo. This achievement underscores its effectiveness in chatbot systems developed from language models, particularly when utilizing high-quality data distilled from sources like ChatGPT/GPT-4.
The core of Starling-7B's success lies in its unique dataset, Nectar, the first of its kind, offering 183K chat prompts with 7 responses each from various models, resulting in 3.8M pairwise comparisons. This dataset is specially crafted to mitigate positional bias in GPT-4-based rankings, a crucial step in ensuring the quality and reliability of the data.
In addition to the language model, the Starling-RM-7B-alpha reward model, trained on the Nectar dataset, plays a vital role in refining the chatbot's helpfulness. The reward model and language model are open-sourced, aiding the deepening of understanding in RLHF mechanisms and contributing to AI safety research.
Despite its advancements, Starling-7B, like other small-sized LLMs, faces challenges in tasks involving reasoning or mathematics and may generate verbose content at times. It also shows susceptibility to jailbreaking prompts. Nonetheless, the team behind Starling-7B is committed to its continual improvement, exploring new training methods for both the reward and language models, and inviting the community to collaborate in enhancing these models.

No comments:
Post a Comment